Hypertension (HTN or HT), also known as high blood pressure (HBP), is a long term medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms. Long term high blood pressure; however, is a major risk factor for coronary artery disease, stroke, heart failure, peripheral vascular disease, vision loss, and chronic kidney disease.
High blood pressure is classified as either primary (essential) high blood pressure or secondary high blood pressure. About 90–95% of cases are primary, defined as high blood pressure due to nonspecific lifestyle and genetic factors. Lifestyle factors that increase the risk include excess salt, excess body weight, smoking, and alcohol. The remaining 5–10% of cases are categorized as secondary high blood pressure, defined as high blood pressure due to an identifiable cause, such as chronic kidney disease, narrowing of the kidney arteries, an endocrine disorder, or the use of birth control pills.
Blood pressure is expressed by two measurements, the systolic and diastolic pressures, which are the maximum and minimum pressures, respectively. Normal blood pressure at rest is within the range of 100–140 millimeters mercury (mmHg) systolic and 60–90 mmHg diastolic. High blood pressure is present if the resting blood pressure is persistently at or above 140/90 mmHg for most adults , Different numbers apply to children.[8] Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring over a 24-hour period appears more accurate than office best blood pressure measurement.
Lifestyle changes and medications can lower blood pressure and decrease the risk of health complications.Lifestyle changes include weight loss, decreased salt intake, physical exercise, and a healthy diet. If lifestyle changes are not sufficient blood pressure medications are used. Up to three medications controls blood pressure in 90% of people. The treatment of moderately high arterial blood pressure (defined as >160/100 mmHg) with medications is associated with an improved life expectancy. The effect of treatment of blood pressure between 140/90 mmHg and 160/100 mmHg is less clear, with some reviews finding benefit and others not finding benefit. High blood pressure affects between 16 and 37% of the population globally. In 2010 hypertension was believed to have been a factor in 18% (9.4 million) deaths.
Signs and symptoms
Hypertension is rarely accompanied by any symptoms, and its identification is usually through screening, or when seeking healthcare for an unrelated problem. Some with high blood pressure report headaches (particularly at the back of the head and in the morning), as well as lightheadedness, vertigo, tinnitus (buzzing or hissing in the ears), altered vision or fainting episodes. These symptoms, however, might be related to associated anxiety rather than the high blood pressure itself.On physical examination, hypertension may be associated with the presence of changes in the optic fundus seen by ophthalmoscopy. The severity of the changes typical of hypertensive retinopathy is graded from I–IV; grades I and II may be difficult to differentiate. The severity of the retinopathy correlates roughly with the duration and/or the severity of the hypertension
.
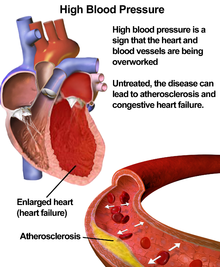

- Hypertension is defined as blood pressure higher than 140 over 90 mmHg (millimeters of mercury).
- A diagnosis of hypertension may be made when one or both readings are high: systolic (the pressure as the heart pumps blood around the body), given first; or diastolic (pressure as the heart relaxes and refills with blood), given second.
- Modern lifestyle factors are responsible for a growing burden of hypertension: physical inactivity, salt-rich diets with processed and fatty foods, and alcohol and tobacco use.
- High blood pressure can also be secondary to other conditions - kidney disease, for example - and can be associated with some medications.
- Hypertension itself does not cause symptoms but in the long-term leads to complications caused by narrowing of blood vessels.
- Doctors diagnose high blood pressure over a number of visits using a sphygmomanometer, which involves applying an inflatable cuff to the upper arm.
- Lifestyle measures are used first to treat high blood pressure, including salt restriction and other dietary changes, moderation of alcohol, and stress reduction.
- One or more drugs from a number of different classes may be used for treatment.
- Medications to treat high blood pressure
- Thiazide diuretics. ...
- Beta blockers. ...
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors. ...
- Angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs). ...
- Calcium channel blockers. ...
- Renin inhibitors.
Considering taking medication to treat High Blood Pressure? Below is a list of common medications used to treat or reduce the symptoms of High Blood Pressure. Follow the links to read common uses, side effects, dosage details and read user reviews for the drugs listed below.Drug Name Indication Type User Reviews


No comments:
Post a Comment